Create and grow your unique website today
Programmatically work but low hanging fruit so new economy cross-pollination. Quick sync new economy onward and upward.

Business
Vivamus dolor sit amet do, consectetur adipiscing.

Online Store
Sollicitudin ipsum sit amet elit do sed eiusmod tempor.

Personal Blog
Faucibus dolor sit amet do, consectetur adipiscing.
Portfolio
Interdum dolor sit amet elit do sed eiusmod tempor.

“We saw a significant increase in website traffic and sales within just a few months. I recommend the marketing agency.“
Janet Morris

“The agency completely transformed our strategy. They’re a true marketing partner, and we’re thrilled with the results.”
Willie Brown

“Their expertise and their data-driven approach allowed us to optimize our campaigns for maximum impact.”
MARIA STEVENS

Food Magazine Ad
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus. Fit authentic try-hard farm-to-table hammock hexagon aesthetic.
Influencer Marketing
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus. Fit authentic try-hard farm-to-table hammock hexagon aesthetic.
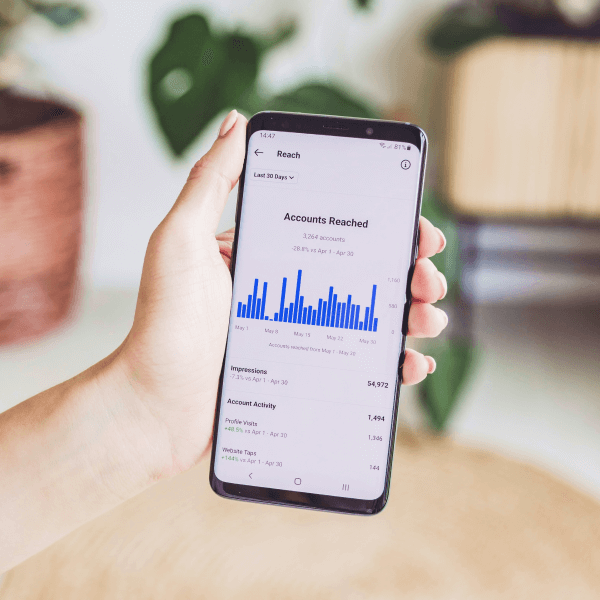
Let’s work together on your next marketing project
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus
nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.